Does Melatonin Affect GABA Activity in the Brain?

The Anxiety and Depression Association of America claims that General Anxiety Disorder (GAD) affects up to 6 million people, as does Panic Disorder (PD), while Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) affects 15 million people. Sleep disorders and anxiety can occur together, each amplifying the detrimental effects of the other. It’s hard to sleep if you’re anxious and if you haven’t had enough sleep, your body doesn’t have the support it needs to keep anxiety at bay.
With so many people affected by sleep and anxiety disorders, it is a given that they will look for relief, many from more natural sources than pharmaceuticals. With that in mind, here is an overview of melatonin and GABA, two popular supplements for sleep and anxiety respectively, and how they may work together for even greater effect.
Table of Contents
The Role of Melatonin in Sleep
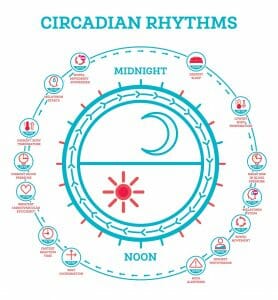
This chart will help you to understand the physical components of the circadian rhythm. Notice that melatonin production tends to begin around 9:00 pm and cease at 7:30 am.
If you’ve had any trouble with your sleep habits, you’ve likely heard of melatonin. A naturally produced hormone, melatonin plays a vital role in the body’s circadian rhythm.
In a perfect system, the pineal gland secretes melatonin when exposed to darkness, gradually producing sleepiness. A problem occurs when we are exposed to a lot of light at night, especially from blue light emitting devices (we’re looking at you phones and laptops) interfering with our natural sleep-wake cycles. The artificial light interrupts this process, possibly reducing melatonin production.
In an effort to combat this disruption, some people supplement their routines with melatonin. Taken at night, just as your body would naturally produce it, there is considerable evidence to back up the use of melatonin to try and get your sleep habits back on track.
Melatonin may be involved in many other systemic functions, including the immune response, reducing oxidative stress, and the reduction of melatonin in the body may encourage tumor growth. In addition to these potential benefits, “unequivocal evidence of its efficacy has been established for a few conditions — jet lag, depression, and insomnia.” (1)
With anxiety, the results are slightly less concrete. There is evidence that melatonin is as effective as Midazolam, a prescription benzodiazepine, in treating pre-operative anxiety (2) but its effectiveness in post-operative anxiety was less.
In a 2018 study, the researchers concluded that melatonin has the ability to reduce anxiety behaviors in rats. While that’s interesting enough on its own, what is truly interesting is that it seems to work by interacting with the GABA receptors in the brain. (3)
What is GABA?
Short for Gamma-Aminobutyric acid, GABA is a naturally produced amino acid. It’s essential role in the body is to reduce the activity of neurons and the central nervous system, promoting relaxation. It also plays a role in pain relief, reducing the feelings of stress and anxiety, and sleep.
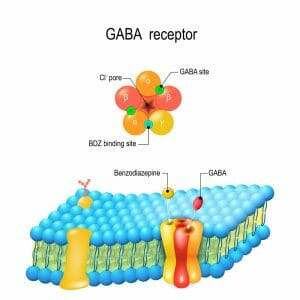
When combined with glutamate, it may play a role in increasing muscle tone. It is also thought to stimulate the production of growth hormones. These effects may explain its popularity with athletes.
Since it is so critical, many pharmaceuticals are aimed at the GABA receptors in the brain, and many natural supplements aimed at reducing stress or sleep include GABA as an ingredient. It occurs naturally in black and green teas and in fermented foods.
Does Melatonin Affect GABA Activity in the Brain?
Because of their presence in the body, as well as the prevalence of GABA related drugs and melatonin supplementation, it makes sense that scientists are starting to look at how the combination of melatonin and GABA together.
While it’s a relatively new avenue of study, melatonin seems to work synergistically with GABA, exciting the brain’s GABA receptors and increasing their sensitivity to GABA. Researchers have noted that melatonin’s anti-anxiety and sedative effects can be attributed to the ability of its metabolite (a substance that is necessary for metabolism) to stimulate GABA-benzodiazapene receptors. (4)
This research is exciting for those millions of people who suffer with sleep and/or anxiety disorders as it shows there just may be relief in sight.

Click here to experience one of the most potent melatonin formulations on the market.
Thank you for taking the time to read Does Melatonin Affect GABA Activity in the Brain
Please note: All information presented to you in this website is intended for your general knowledge only and is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment for specific medical conditions. We cannot, and will not give you medical advice. We strongly recommend you consult your physician for any and all specific health issues. If you have any questions or contributions, please contact us via email or phone-call. We are constantly looking for new information to promote wellness – and hearing from you would make our day.
Live Vibrantly!
References:
- The Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin: A Review of the Science
- Melatonin for pre‐ and postoperative anxiety in adults
- Melatonin prevents sleep deprivation-associated anxiety-like behavior in rats: role of oxidative stress and balance between GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission
- Melatonin modulates the GABAergic response in cultured rat hippocampal neurons

